Go To
- Power BI forums
- Updates
- News & Announcements
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Power Platform Integration - Better Together!
- Power Platform Integrations (Read-only)
- Power Platform and Dynamics 365 Integrations (Read-only)
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Community Connections & How-To Videos
- COVID-19 Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- 2021 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2020 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2019 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- Events
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
- Community Blog
- Power BI Community Blog
- Custom Visuals Community Blog
- Community Support
- Community Accounts & Registration
- Using the Community
- Community Feedback
Turn on suggestions
Auto-suggest helps you quickly narrow down your search results by suggesting possible matches as you type.
Showing results for
Register now to learn Fabric in free live sessions led by the best Microsoft experts. From Apr 16 to May 9, in English and Spanish.
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Developer
- Power BI custom data connector PostgeSQL
Reply
Topic Options
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Power BI custom data connector PostgeSQL
04-09-2019
03:35 AM
I can directly connect to PostgreSQL from native Power BI connector. I want to deveop a custom data connector to enable direct query.
I installed the odbc driver (32 bit and 64 bit just to be on the safe side) downloaded the sample from https://github.com/Microsoft/DataConnectors/tree/master/samples/ODBC/SqlODBC
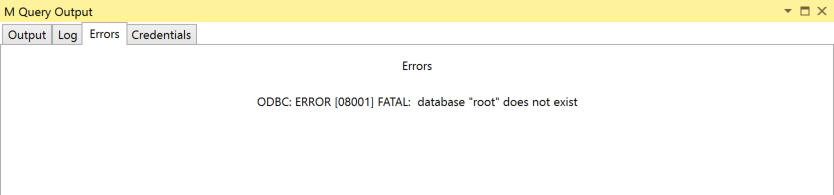
After confuring it i get an error as bellow. Any suggestions
The power query file is given bellow
// This connector provides a sample Direct Query enabled connector
// based on an ODBC driver. It is meant as a template for other
// ODBC based connectors that require similar functionality.
//
section SqlODBC;
// When set to true, additional trace information will be written out to the User log.
// This should be set to false before release. Tracing is done through a call to
// Diagnostics.LogValue(). When EnableTraceOutput is set to false, the call becomes a
// no-op and simply returns the original value.
EnableTraceOutput = true;
// TODO
// add and handle common options record properties
// add handling for LIMIT/OFFSET vs. TOP
// add handling for SSL
/****************************
* ODBC Driver Configuration
****************************/
// The name of your ODBC driver.
//
Config_DriverName = "PostgreSQL Unicode";
// If your driver under-reports its SQL conformance level because it does not
// support the full range of CRUD operations, but does support the ANSI SQL required
// to support the SELECT operations performed by Power Query, you can override
// this value to report a higher conformance level. Please use one of the numeric
// values below (i.e. 8 for SQL_SC_SQL92_FULL).
//
// SQL_SC =
// [
// SQL_SC_SQL92_ENTRY = 1,
// SQL_SC_FIPS127_2_TRANSITIONAL = 2,
// SQL_SC_SQL92_INTERMEDIATE = 4,
// SQL_SC_SQL92_FULL = 8
// ]
//
// Set to null to determine the value from the driver.
//
Config_SqlConformance = ODBC[SQL_SC][SQL_SC_SQL92_FULL]; // null, 1, 2, 4, 8
// Set this option to true if your ODBC supports the standard username/password
// handling through the UN and PWD connection string parameters. If the user
// selects UsernamePassword auth, the supplied values will be automatically
// added to the CredentialConnectionString.
//
// If you wish to set these values yourself, or your driver requires additional
// parameters to be set, please set this option to 'false'
//
Config_DefaultUsernamePasswordHandling = true; // true, false
// Some drivers have problems will parameter bindings and certain data types.
// If the driver supports parameter bindings, then set this to true.
// When set to false, parameter values will be inlined as literals into the generated SQL.
// To enable inlining for a limited number of data types, set this value
// to null and set individual flags through the SqlCapabilities record.
//
// Set to null to determine the value from the driver.
//
Config_UseParameterBindings = false; // true, false, null
// Override this setting to force the character escape value.
// This is typically done when you have set UseParameterBindings to false.
//
// Set to null to determine the value from the driver.
//
Config_StringLiterateEscapeCharacters = { "\" }; // ex. { "\" }
// Override this if the driver expects the use of CAST instead of CONVERT.
// By default, the query will be generated using ANSI SQL CONVERT syntax.
//
// Set to false or null to leave default behavior.
//
Config_UseCastInsteadOfConvert = null; // true, false, null
// If the driver supports the TOP clause in select statements, set this to true.
// If set to false, you MUST implement the AstVisitor for the LimitClause in the
// main body of the code below.
//
Config_SupportsTop = false; // true, false
// Set this to true to enable Direct Query in addition to Import mode.
//
Config_EnableDirectQuery = true; // true, false
[DataSource.Kind="SqlODBC", Publish="SqlODBC.Publish"]
shared SqlODBC.Contents = (server as text) =>
let
//
// Connection string settings
//
ConnectionString = [
Driver = Config_DriverName,
// set all connection string properties
Server = server,
ApplicationIntent = "readonly"
],
//
// Handle credentials
// Credentials are not persisted with the query and are set through a separate
// record field - CredentialConnectionString. The base Odbc.DataSource function
// will handle UsernamePassword authentication automatically, but it is explictly
// handled here as an example.
//
Credential = Extension.CurrentCredential(),
CredentialConnectionString =
if Credential[AuthenticationKind]? = "UsernamePassword" then
// set connection string parameters used for basic authentication
[ UID = Credential[Username], PWD = Credential[Password] ]
else if (Credential[AuthenticationKind]? = "Windows") then
// set connection string parameters used for windows/kerberos authentication
[ Trusted_Connection="Yes" ]
else
error Error.Record("Error", "Unhandled authentication kind: " & Credential[AuthenticationKind]?),
//
// Configuration options for the call to Odbc.DataSource
//
defaultConfig = BuildOdbcConfig(),
SqlCapabilities = defaultConfig[SqlCapabilities] & [
// place custom overrides here
FractionalSecondsScale = 3
],
// Please refer to the ODBC specification for SQLGetInfo properties and values.
// https://github.com/Microsoft/ODBC-Specification/blob/master/Windows/inc/sqlext.h
SQLGetInfo = defaultConfig[SQLGetInfo] & [
// place custom overrides here
SQL_SQL92_PREDICATES = ODBC[SQL_SP][All],
SQL_AGGREGATE_FUNCTIONS = ODBC[SQL_AF][All]
],
// SQLGetTypeInfo can be specified in two ways:
// 1. A #table() value that returns the same type information as an ODBC
// call to SQLGetTypeInfo.
// 2. A function that accepts a table argument, and returns a table. The
// argument will contain the original results of the ODBC call to SQLGetTypeInfo.
// Your function implementation can modify/add to this table.
//
// For details of the format of the types table parameter and expected return value,
// please see: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/odbc/reference/syntax/sqlgettypeinfo-function
//
// The sample implementation provided here will simply output the original table
// to the user trace log, without any modification.
SQLGetTypeInfo = (types) =>
if (EnableTraceOutput <> true) then types else
let
// Outputting the entire table might be too large, and result in the value being truncated.
// We can output a row at a time instead with Table.TransformRows()
rows = Table.TransformRows(types, each Diagnostics.LogValue("SQLGetTypeInfo " & _[TYPE_NAME], _)),
toTable = Table.FromRecords(rows)
in
Value.ReplaceType(toTable, Value.Type(types)),
// SQLColumns is a function handler that receives the results of an ODBC call
// to SQLColumns(). The source parameter contains a table with the data type
// information. This override is typically used to fix up data type mismatches
// between calls to SQLGetTypeInfo and SQLColumns.
//
// For details of the format of the source table parameter, please see:
// https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/odbc/reference/syntax/sqlcolumns-function
//
// The sample implementation provided here will simply output the original table
// to the user trace log, without any modification.
SQLColumns = (catalogName, schemaName, tableName, columnName, source) =>
if (EnableTraceOutput <> true) then source else
// the if statement conditions will force the values to evaluated/written to diagnostics
if (Diagnostics.LogValue("SQLColumns.TableName", tableName) <> "***" and Diagnostics.LogValue("SQLColumns.ColumnName", columnName) <> "***") then
let
// Outputting the entire table might be too large, and result in the value being truncated.
// We can output a row at a time instead with Table.TransformRows()
rows = Table.TransformRows(source, each Diagnostics.LogValue("SQLColumns", _)),
toTable = Table.FromRecords(rows)
in
Value.ReplaceType(toTable, Value.Type(source))
else
source,
// This record allows you to customize the generated SQL for certain
// operations. The most common usage is to define syntax for LIMIT/OFFSET operators
// when TOP is not supported.
//
AstVisitor = [
LimitClause = (skip, take) =>
let
offset = if (skip <> null and skip > 0) then Text.Format("OFFSET #{0} ROWS", {skip}) else "",
limit = if (take <> null) then Text.Format("LIMIT #{0}", {take}) else ""
in
[
Text = Text.Format("#{0} #{1}", {offset, limit}),
Location = "AfterQuerySpecification"
]
],
OdbcDatasource = Odbc.DataSource(ConnectionString, [
// A logical (true/false) that sets whether to view the tables grouped by their schema names
HierarchicalNavigation = true,
// Prevents execution of native SQL statements. Extensions should set this to true.
HideNativeQuery = true,
// Allows upconversion of numeric types
SoftNumbers = true,
// Allow upconversion / resizing of numeric and string types
TolerateConcatOverflow = true,
// Enables connection pooling via the system ODBC manager
ClientConnectionPooling = true,
// These values should be set by previous steps
CredentialConnectionString = CredentialConnectionString,
//AstVisitor = AstVisitor,
SqlCapabilities = SqlCapabilities,
SQLColumns = SQLColumns,
SQLGetInfo = SQLGetInfo,
SQLGetTypeInfo = SQLGetTypeInfo
])
in
OdbcDatasource;
// Data Source Kind description
SqlODBC = [
// Set the TestConnection handler to enable gateway support.
// The TestConnection handler will invoke your data source function to
// validate the credentials the user has provider. Ideally, this is not
// an expensive operation to perform. By default, the dataSourcePath value
// will be a json string containing the required parameters of your data
// source function. These should be parsed and parsed as individual parameters
// to the specified data source function.
TestConnection = (dataSourcePath) =>
let
json = Json.Document(dataSourcePath),
server = json[server] // name of function parameter
in
{ "SqlODBC.Contents", server },
// Set supported types of authentication
Authentication = [
Windows = [],
UsernamePassword = []
],
Label = Extension.LoadString("DataSourceLabel")
];
// Data Source UI publishing description
SqlODBC.Publish = [
Beta = true,
Category = "Other",
ButtonText = { Extension.LoadString("ButtonTitle"), Extension.LoadString("ButtonHelp") },
LearnMoreUrl = "https://powerbi.microsoft.com/",
SupportsDirectQuery = Config_EnableDirectQuery,
SourceImage = SqlODBC.Icons,
SourceTypeImage = SqlODBC.Icons
];
SqlODBC.Icons = [
Icon16 = { Extension.Contents("SqlODBC16.png"), Extension.Contents("SqlODBC20.png"), Extension.Contents("SqlODBC24.png"), Extension.Contents("SqlODBC32.png") },
Icon32 = { Extension.Contents("SqlODBC32.png"), Extension.Contents("SqlODBC40.png"), Extension.Contents("SqlODBC48.png"), Extension.Contents("SqlODBC64.png") }
];
// build settings based on configuration variables
BuildOdbcConfig = () as record =>
let
defaultConfig = [
SqlCapabilities = [],
SQLGetFunctions = [],
SQLGetInfo = []
],
withParams =
if (Config_UseParameterBindings = false) then
let
caps = defaultConfig[SqlCapabilities] & [
SqlCapabilities = [
SupportsNumericLiterals = true,
SupportsStringLiterals = true,
SupportsOdbcDateLiterals = true,
SupportsOdbcTimeLiterals = true,
SupportsOdbcTimestampLiterals = true
]
],
funcs = defaultConfig[SQLGetFunctions] & [
SQLGetFunctions = [
SQL_API_SQLBINDPARAMETER = false
]
]
in
defaultConfig & caps & funcs
else
defaultConfig,
withEscape =
if (Config_StringLiterateEscapeCharacters <> null) then
let
caps = withParams[SqlCapabilities] & [
SqlCapabilities = [
StringLiteralEscapeCharacters = Config_StringLiterateEscapeCharacters
]
]
in
withParams & caps
else
withParams,
withTop =
let
caps = withEscape[SqlCapabilities] & [
SqlCapabilities = [
SupportsTop = Config_SupportsTop
]
]
in
withEscape & caps,
withCastOrConvert =
if (Config_UseCastInsteadOfConvert = true) then
let
caps = withTop[SQLGetFunctions] & [
SQLGetFunctions = [
SQL_CONVERT_FUNCTIONS = 0x2 /* SQL_FN_CVT_CAST */
]
]
in
withTop & caps
else
withTop,
withSqlConformance =
if (Config_SqlConformance <> null) then
let
caps = withCastOrConvert[SQLGetInfo] & [
SQLGetInfo = [
SQL_SQL_CONFORMANCE = Config_SqlConformance
]
]
in
withCastOrConvert & caps
else
withCastOrConvert
in
withSqlConformance;
//
// Load common library functions
//
Extension.LoadFunction = (name as text) =>
let
binary = Extension.Contents(name),
asText = Text.FromBinary(binary)
in
Expression.Evaluate(asText, #shared);
// Diagnostics module contains multiple functions. We can take the ones we need.
Diagnostics = Extension.LoadFunction("Diagnostics.pqm");
Diagnostics.LogValue = if (EnableTraceOutput) then Diagnostics[LogValue] else (prefix, value) => value;
// OdbcConstants contains numeric constants from the ODBC header files, and a
// helper function to create bitfield values.
ODBC = Extension.LoadFunction("OdbcConstants.pqm");
Odbc.Flags = ODBC[Flags];
0 REPLIES 0
Helpful resources
Announcements

Microsoft Fabric Learn Together
Covering the world! 9:00-10:30 AM Sydney, 4:00-5:30 PM CET (Paris/Berlin), 7:00-8:30 PM Mexico City

Power BI Monthly Update - April 2024
Check out the April 2024 Power BI update to learn about new features.

Top Solution Authors
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 14 | |
| 2 | |
| 2 | |
| 1 | |
| 1 |