- Power BI forums
- Updates
- News & Announcements
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Service
- Report Server
- Power Query
- Mobile Apps
- Developer
- DAX Commands and Tips
- Custom Visuals Development Discussion
- Health and Life Sciences
- Power BI Spanish forums
- Translated Spanish Desktop
- Power Platform Integration - Better Together!
- Power Platform Integrations (Read-only)
- Power Platform and Dynamics 365 Integrations (Read-only)
- Training and Consulting
- Instructor Led Training
- Dashboard in a Day for Women, by Women
- Galleries
- Community Connections & How-To Videos
- COVID-19 Data Stories Gallery
- Themes Gallery
- Data Stories Gallery
- R Script Showcase
- Webinars and Video Gallery
- Quick Measures Gallery
- 2021 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2020 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- 2019 MSBizAppsSummit Gallery
- Events
- Ideas
- Custom Visuals Ideas
- Issues
- Issues
- Events
- Upcoming Events
- Community Blog
- Power BI Community Blog
- Custom Visuals Community Blog
- Community Support
- Community Accounts & Registration
- Using the Community
- Community Feedback
Register now to learn Fabric in free live sessions led by the best Microsoft experts. From Apr 16 to May 9, in English and Spanish.
- Power BI forums
- Forums
- Get Help with Power BI
- Desktop
- Moving Average
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
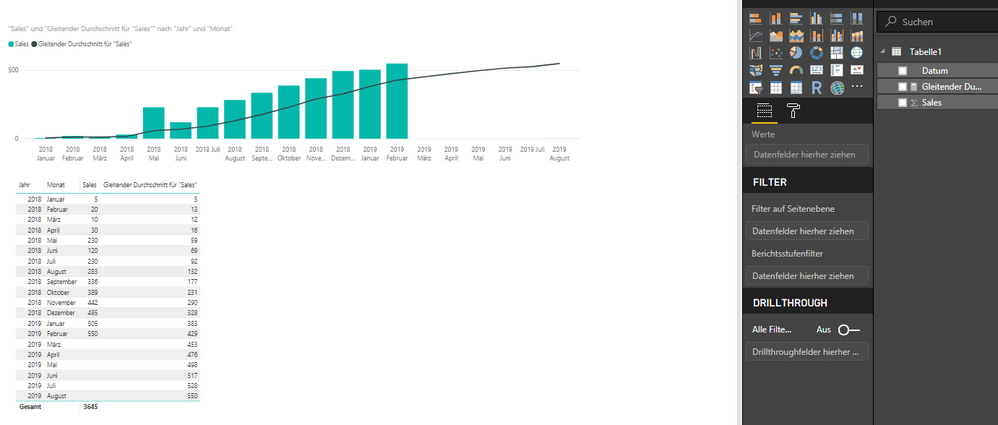
Moving Average
Hey,
I tried to go for the Moving Average building with PowerBI.
The problem is that the moving average is calculated for the future, which does not make any sense.
I wanted to do a six-month-rolling average with the quick measure (problem of above appeared), then with the formula = calculate(average([Sales]), DatesInPeriod([date];Lastdate([date]), -6, MONTH). Same Problem, again. So I do not know what is the problem. Perhaps somebody could offer me a simple sample PBIX data with a 6 month moving average over 2 years data..
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Rotergnom2,
I would suggest you create a date table in your scenario. Please check out the attached demo and the measure below.
Measure =
VAR maxFactDate =
CALCULATE ( MAX ( FactTable[Date] ), ALL ( 'Calendar' ) )
RETURN
IF (
MAX ( 'Calendar'[Date] ) > maxFactDate,
BLANK (),
CALCULATE (
AVERAGEX (
SUMMARIZE (
'FactTable',
'Calendar'[Date].[Year],
'Calendar'[Date].[Month],
"MonthTotal", SUM ( FactTable[Sales] )
),
[MonthTotal]
),
DATESINPERIOD ( 'Calendar'[date], LASTDATE ( 'Calendar'[date] ), -6, MONTH )
)
)
Best Regards,
Dale
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Rotergnom2,
Could you please mark the proper answer as a solution?
Best Regards,
Dale
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Hi @Rotergnom2,
I would suggest you create a date table in your scenario. Please check out the attached demo and the measure below.
Measure =
VAR maxFactDate =
CALCULATE ( MAX ( FactTable[Date] ), ALL ( 'Calendar' ) )
RETURN
IF (
MAX ( 'Calendar'[Date] ) > maxFactDate,
BLANK (),
CALCULATE (
AVERAGEX (
SUMMARIZE (
'FactTable',
'Calendar'[Date].[Year],
'Calendar'[Date].[Month],
"MonthTotal", SUM ( FactTable[Sales] )
),
[MonthTotal]
),
DATESINPERIOD ( 'Calendar'[date], LASTDATE ( 'Calendar'[date] ), -6, MONTH )
)
)
Best Regards,
Dale
If this post helps, then please consider Accept it as the solution to help the other members find it more quickly.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
So, is your calculation correct other than the fact that it includes future estimations?
@ me in replies or I'll lose your thread!!!
Instead of a Kudo, please vote for this idea
Become an expert!: Enterprise DNA
External Tools: MSHGQM
YouTube Channel!: Microsoft Hates Greg
Latest book!: The Definitive Guide to Power Query (M)
DAX is easy, CALCULATE makes DAX hard...
Helpful resources

Microsoft Fabric Learn Together
Covering the world! 9:00-10:30 AM Sydney, 4:00-5:30 PM CET (Paris/Berlin), 7:00-8:30 PM Mexico City

Power BI Monthly Update - April 2024
Check out the April 2024 Power BI update to learn about new features.

| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 110 | |
| 97 | |
| 78 | |
| 64 | |
| 55 |
| User | Count |
|---|---|
| 143 | |
| 109 | |
| 89 | |
| 84 | |
| 66 |